Gemini News Archive
Spectacular Star Cluster May Host Black Hole Missing Link
Press Release | 2008 April 2
The well-known naked-eye star cluster Omega Centauri may be home to an elusive intermediate-mass black hole. Observations made using Gemini Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope provide convincing evidence that such black holes do exist and could even lead to an understanding of how they might evolve into larger supermassive black holes.
Supernova Remnants Dance in the LMC
Press Release | 2008 January 8
The Gemini South Multi-Object Spectograph (GMOS) recently captured a dramatic image of a vast cloud complex named DEM L316 located in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Odd Little Star has Magnetic Personality
Press Release | 2007 November 28
Simultaneous observations made by four of the most powerful Earth- and space-based telescopes revealed an unusually active magnetic field on the ultracool low-mass star TVLM513-46546.
Astronomers Spot Evidence for Colliding Planet Embryos in Famous Star Cluster
Press Release | 2007 November 14
Astronomers have found evidence for the formation of young rocky planets around the star HD 23514 located in the well-known Pleiades (Seven Sisters) star cluster that is easily visible in the current evening sky.
Charon: An Ice Machine in the Ultimate Deep Freeze
Press Release | 2007 July 17
NIRI observations with AO showed evidence of frigid geysers spewing material up through cracks in the crust of Pluto's companion Charon and recoating parts of its surface in ice crystals.
Discovery Narrows the Gap Between Planets and Brown Dwarfs
Press Release | 2007 May 30
The coolest-known star-like object, called ULAS J0034-00 and located in the constellation Cetus, has a record-setting surface temperature of 600-700 K, cooler than any known solitary brown dwarf.
Featherweight Celestial Pair Has Uncertain Future Together
Press Release | 2007 April 4
Astronomers have serendipitously discovered a record-breaking pair of low-mass objects with an extreme orbital separation. The petite objects, each of which has a mass less than 100 times that of Jupiter, are separated by more than 5,000 times the distance between the Sun and Earth
The Delicate Trails of Star Birth
Press Release | 2007 March 22
An image released today by the Gemini Observatory brings into focus a new and remarkably detailed view of supersonic "bullets" of gas and the wakes created as they pierce through clouds of molecular hydrogen in the Orion Nebula.
Some Rare Abnormal Stars may have White Dwarf Parents to Blame
Press Release | 2007 January 8
Astronomers have announced the discovery of huge quantities of an unusual variety of oxygen in two very rare types of stars, suggesting that the origin of these oddball stars may lie in the physics behind the mergers of white dwarf star pairs.
Small Warm Doughnut Feeds Theories of Extragalactic Black Holes
Press Release | 2007 January 8
An international team of astronomers used a novel approach to peer deeply into the energetic core of the nearby galaxy Centaurus A and set stringent constraints on its size and characteristics, indicating that it is likely quite petite and clumpy.
Gemini Captures Close Encounter of Jupiter's Red Spots
Press Release | 2006 July 20
Gemini North adaptive optics image of Jupiter and its two red spots (which appear white because this is a near-infrared image; in visible light they appear reddish).
THE EARLY UNIVERSE IS DUSTY, AND ASTRONOMERS FINALLY KNOW WHY
Press Release | 2006 June 8
Massive star supernovae have been major "dust factories" ever since the first generations of stars formed several hundred million years after the Big Bang, according to an international study.
GEMINI PROBES THE CENTER OF ANDROMEDA GALAXY WITH UNPRECEDENTED CLARITY
Press Release | 2006 June 5
Gemini observations reveal an intriguing dust-enshrouded star near the core of the galaxy M31, while extremely sharp adaptive optics images allowed the analysis of thousands of individual stars that indicates a long-stable environment around the galaxy’s core.
A Tale of Two Nebulae
Press Release | 2006 June 4
Two new images from Gemini Observatory released today show a pair of beautiful nebulae that were created by two very different types of stars at what may be similar points in their evolutionary timelines.
Companion Explains "Chameleon" Supernova
Press Release | 2006 May 3
Using the Gemini South telescope in Chile, Australian astronomers have found a predicted "companion" star left behind when its partner exploded as a very unusual supernova.
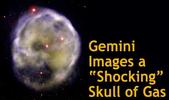
Gemini Images a "Shocking" Skull of Gas
Press Release | 2006 April 7
A new Gemini Observatory image of NGC 246, nicknamed the "Skull Nebula," shows what can happen as the outer atmosphere of a fast-moving, dying star lpushes through the complex soufflé of gas and dust that lies between the stars of our galaxy.
Gemini Looks Down the Mouth of an Interstellar Cavern
Press Release | 2006 January 4
Known as the N44 superbubble complex, a storm of billowing clouds blown by the winds from massive stars, and set aglow by their light, is the focus of a striking image released today by Gemini Observatory.
Cracks or Cryovolcanoes? Surface Geology Creates Clouds on Titan as Observed by Gemini and Keck
Press Release | 2005 October 20
Geologic activity on the surface of Saturn's moon Titan is belching puffs of methane gas into the atmosphere of the moon, creating clouds.
Mauna Kea Giants Find Common Nursery for Comets
Press Release | 2005 September 15
A series of coordinated observations, made under ideal conditions by the world’s largest collection of big telescopes, delivered surprising new insights into the ancestry and life cycles of comets.